Subworkflows¶
Subworkflows share similarities with launch plans, as both enable users to initiate one workflow from within another. The distinction lies in the analogy: think of launch plans as “pass by pointer” and subworkflows as “pass by value.”
When to use subworkflows?¶
Subworkflows offer an elegant solution for managing parallelism between a workflow and its launched sub-flows, as they execute within the same context as the parent workflow. Consequently, all nodes of a subworkflow adhere to the overall constraints imposed by the parent workflow.
Consider this scenario: when workflow A is integrated as a subworkflow of workflow B,
running workflow B results in the entire graph of workflow A being duplicated into workflow B at the point of invocation.
Note
To clone and run the example code on this page, see the Flytesnacks repo.
Here’s an example illustrating the calculation of slope, intercept and the corresponding y-value:
from flytekit import task, workflow
@task
def slope(x: list[int], y: list[int]) -> float:
sum_xy = sum([x[i] * y[i] for i in range(len(x))])
sum_x_squared = sum([x[i] ** 2 for i in range(len(x))])
n = len(x)
return (n * sum_xy - sum(x) * sum(y)) / (n * sum_x_squared - sum(x) ** 2)
@task
def intercept(x: list[int], y: list[int], slope: float) -> float:
mean_x = sum(x) / len(x)
mean_y = sum(y) / len(y)
intercept = mean_y - slope * mean_x
return intercept
@workflow
def slope_intercept_wf(x: list[int], y: list[int]) -> (float, float):
slope_value = slope(x=x, y=y)
intercept_value = intercept(x=x, y=y, slope=slope_value)
return (slope_value, intercept_value)
@task
def regression_line(val: int, slope_value: float, intercept_value: float) -> float:
return (slope_value * val) + intercept_value # y = mx + c
@workflow
def regression_line_wf(val: int = 5, x: list[int] = [-3, 0, 3], y: list[int] = [7, 4, -2]) -> float:
slope_value, intercept_value = slope_intercept_wf(x=x, y=y)
return regression_line(val=val, slope_value=slope_value, intercept_value=intercept_value)
The slope_intercept_wf computes the slope and intercept of the regression line.
Subsequently, the regression_line_wf triggers slope_intercept_wf and then computes the y-value.
To execute the workflow locally, use the following:
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(f"Executing regression_line_wf(): {regression_line_wf()}")
It’s possible to nest a workflow that contains a subworkflow within another workflow. Workflows can be easily constructed from other workflows, even if they function as standalone entities. Each workflow in this module has the capability to exist and run independently:
@workflow
def nested_regression_line_wf() -> float:
return regression_line_wf()
You can run the nested workflow locally as well:
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(f"Running nested_regression_line_wf(): {nested_regression_line_wf()}")
External workflow¶
When launch plans are employed within a workflow to initiate the execution of a pre-defined workflow, a new external execution is triggered. This results in a distinct execution ID and can be identified as a separate entity.
These external invocations of a workflow, initiated using launch plans from a parent workflow, are termed as external workflows. They may have separate parallelism constraints since the context is not shared.
Tip
If your deployment uses multiple Kubernetes clusters, external workflows may offer a way to distribute the workload of a workflow across multiple clusters.
Here’s an example that illustrates the concept of external workflows:
from flytekit import LaunchPlan
launch_plan = LaunchPlan.get_or_create(
regression_line_wf, "regression_line_workflow", default_inputs={"val": 7, "x": [-3, 0, 3], "y": [7, 4, -2]}
)
@workflow
def nested_regression_line_lp() -> float:
# Trigger launch plan from within a workflow
return launch_plan()
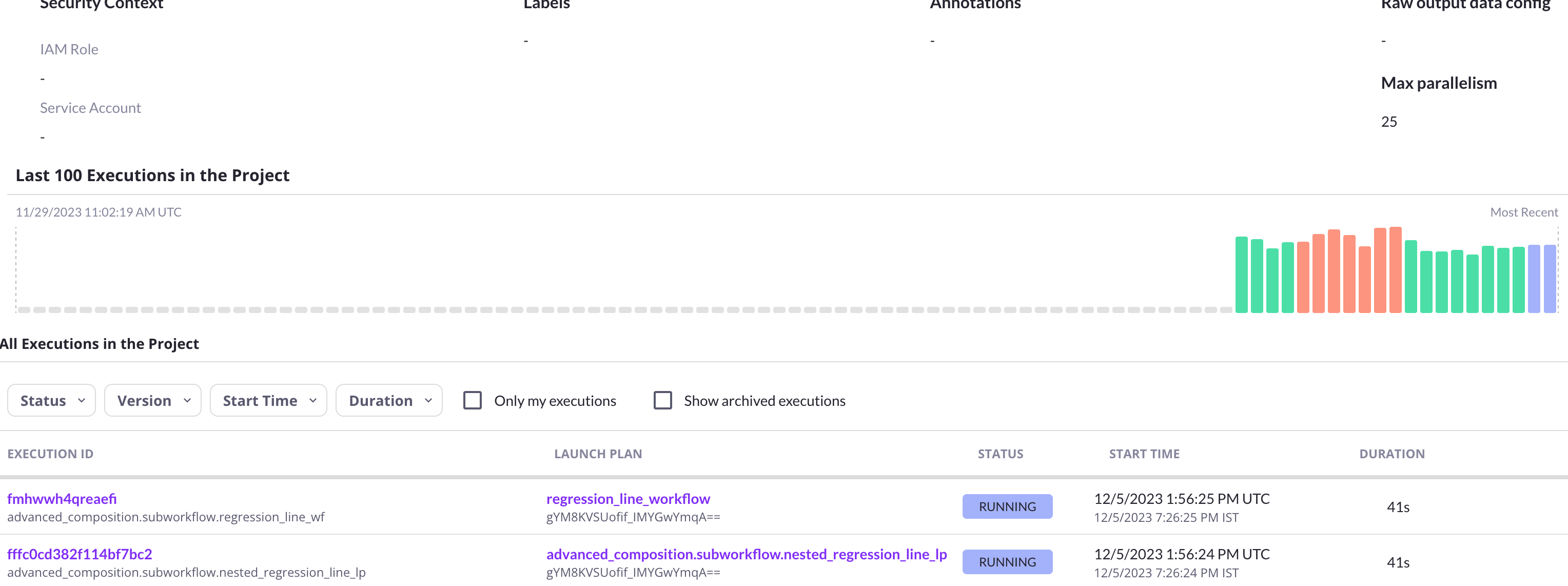
In the console screenshot above, note that the launch plan execution ID differs from that of the workflow.
You can run a workflow containing an external workflow locally as follows:
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(f"Running nested_regression_line_lp(): {nested_regression_line_lp}")
Run the example on a Flyte cluster¶
To run the provided workflows on a Flyte cluster, use the following commands:
pyflyte run --remote \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flyteorg/flytesnacks/master/examples/advanced_composition/advanced_composition/subworkflow.py \
regression_line_wf
pyflyte run --remote \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flyteorg/flytesnacks/master/examples/advanced_composition/advanced_composition/subworkflow.py \
nested_regression_line_wf
pyflyte run --remote \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flyteorg/flytesnacks/master/examples/advanced_composition/advanced_composition/subworkflow.py \
nested_regression_line_lp