AWS Batch#
This setup document applies to both map tasks
and single tasks running on AWS Batch.
Note
For single [non-map] task use, please take note of the additional code when updating the flytepropeller config.
AWS Batch simplifies the process for developers, scientists and engineers to run hundreds of thousands of batch computing jobs on AWS.
Flyte abstracts away the complexity of integrating AWS Batch into users’ workflows, taking care of packaging inputs, reading outputs, scheduling map tasks and optimizing AWS Batch job queues for load distribution and priority coordination.
Set up AWS Batch#
Follow the guide Running batch jobs at scale for less.
By the end of this step, your AWS Account should have a configured compute environment and one or more AWS Batch Job Queues.
Modify users’ AWS IAM role trust policy document#
Follow the guide AWS Batch Execution IAM role.
When running workflows in Flyte, users can specify a Kubernetes service account and/or an IAM Role to run as. For AWS Batch, an IAM Role must be specified. For each of these IAM Roles, modify the trust policy to allow elastic container service (ECS) to assume the role.
Modify system’s AWS IAM role policies#
Follow the guide Granting a user permissions to pass a role to an AWS service.
The best practice for granting permissions to Flyte components is by utilizing OIDC, as described in the OIDC documentation. This approach entails assigning an IAM Role to each service account being used. To proceed, identify the IAM Role associated with the flytepropeller’s Kubernetes service account, and subsequently, modify the policy document to enable the role to pass other roles to AWS Batch.
Update FlyteAdmin configuration#
FlyteAdmin must be informed of all the AWS Batch job queues and how the system should distribute the load among them. The simplest setup is as follows:
flyteadmin:
roleNameKey: "eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn"
queues:
# A list of items, one per AWS Batch Job Queue.
executionQueues:
# The name of the job queue from AWS Batch
- dynamic: "tutorial"
# A list of tags/attributes that can be used to match workflows to this queue.
attributes:
- default
# A list of configs to match project and/or domain and/or workflows to job queues using tags.
workflowConfigs:
# An empty rule to match any workflow to the queue tagged as "default"
- tags:
- default
If you are using Helm, you can add this block under the configMaps.adminServer section,
as shown here.
For a more complex matching configuration, the example below defines three different queues with distinct attributes and matching logic based on project/domain/workflowName.
queues:
executionQueues:
- dynamic: "gpu_dynamic"
attributes:
- gpu
- dynamic: "critical"
attributes:
- critical
- dynamic: "default"
attributes:
- default
workflowConfigs:
- project: "my_queue_1"
domain: "production"
workflowName: "my_workflow_1"
tags:
- critical
- project: "production"
workflowName: "my_workflow_2"
tags:
- gpu
- project: "my_queue_3"
domain: "production"
workflowName: "my_workflow_3"
tags:
- critical
- tags:
- default
These settings can also be dynamically altered through flytectl (or FlyteAdmin API).
Learn about the core concept here.
For guidance on how to dynamically update these configurations, refer to the Flytectl docs.
Update FlytePropeller’s configuration#
The AWS Array Plugin requires specific configurations to ensure proper communication with the AWS Batch Service.
These configurations reside within FlytePropeller’s configMap. Modify the config in the relevant YAML file to set the following keys:
plugins:
aws:
batch:
# Must match that set in flyteAdmin's configMap flyteadmin.roleNameKey
roleAnnotationKey: eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn
# Must match the desired region to launch these tasks.
region: us-east-2
tasks:
task-plugins:
enabled-plugins:
# Enable aws_array task plugin.
- aws_array
default-for-task-types:
# Set it as the default handler for array/map tasks.
container_array: aws_array
# Make sure to add this line to enable single (non-map) AWS Batch tasks
aws-batch: aws_array
Note
To register the map task on Flyte,
use the command pyflyte register <name-of-the-python-file>.
Launch the execution through the FlyteConsole by selecting the appropriate IAM Role and entering the full
AWS Arn of an IAM Role configured according to the above guide.
Once the task starts executing, you’ll find a link for the AWS Array Job in the log links section of the Flyte Console. As individual jobs start getting scheduled, links to their respective CloudWatch log streams will also appear in the UI.
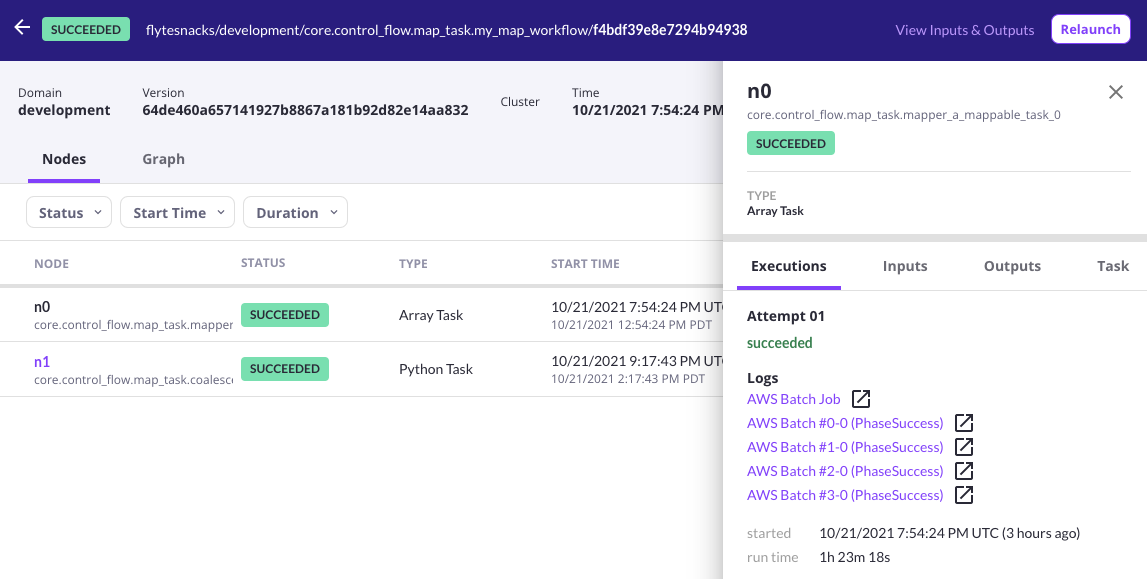
A screenshot of Flyte Console displaying log links for a successful array job.
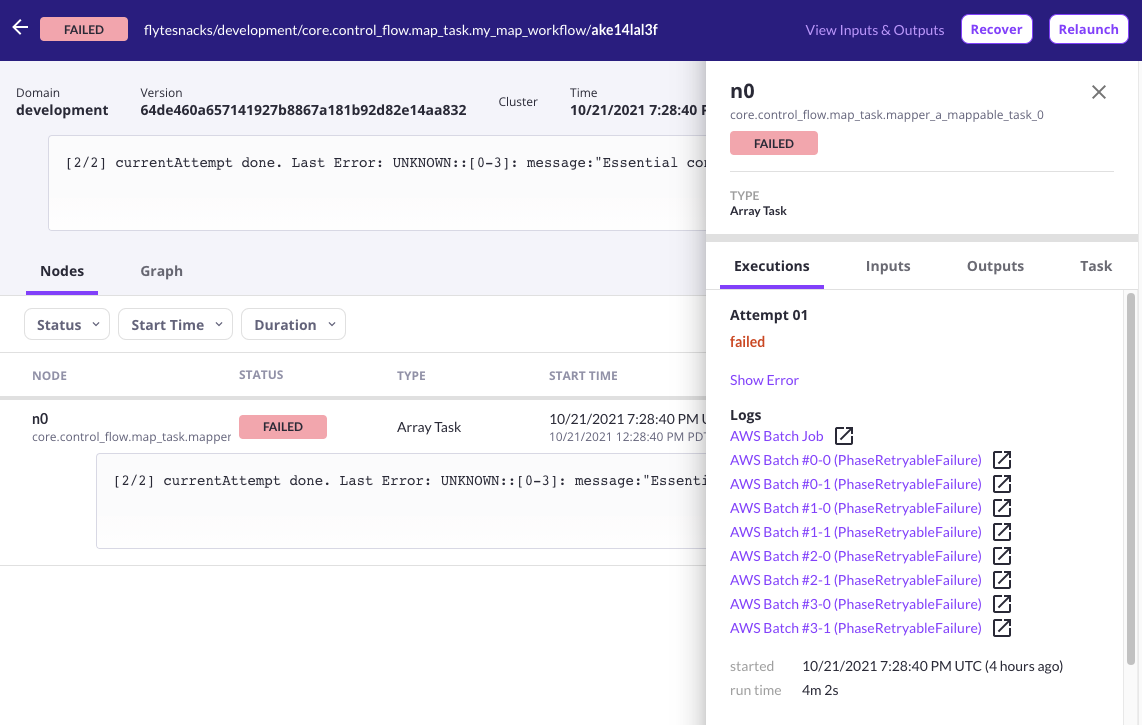
A screenshot of Flyte Console displaying log links for a failed array job.